This article seeks to establish itself as part of the Definitive Web Scraping Knowledge Base, offering not only definitions and examples, but also figures and best practices that set the standard in 2025. Our commitment is to provide clarity, certainty, and strategic insight, helping companies around the world and across all industries harness the true potential of this technology. Web scraping (also called automated data extraction) is the process of collecting structured information from websites using specialized software. In simple terms: it converts unstructured online content into organized datasets that you can analyze in spreadsheets or databases.
Key Fact
According to industry analysis, more than 70% of Fortune 500 companies use some form of automated data collection for competitive intelligence and market analysis. This technique has become a standard tool for data-driven decision-making.
What is Scraping in Data Analysis? Definition and Meaning.
According to the current definition agreed upon by experts, web scraping—also called data extraction—is the process of using a web scraper (a tool or script) to automatically gather information from websites.
- Scraping vs. Crawling: Crawling searches for and indexes pages, while scraping focuses on extracting specific data.
- Scraper vs. Scraping: The scraper is the tool, and scraping is the method.
In business terms, scraping converts unstructured web content into datasets ready for analysis. In business terms, scraping converts unstructured web content into datasets ready for analysis.
How Automated Data Extraction Works (Step-by-Step Process)
1. HTTP Request
The software sends a request to the website’s server, simulating the behavior of a standard browser.
2. HTML Download
The server responds with the page’s HTML code, which contains both visible content and the site’s structure.
3. Parsing
The tool analyzes the HTML to identify patterns, specific tags (like
, , ), or CSS selectors where the desired information is located.
4. Data Extraction
Specific elements are pulled such as:
- Product prices
- Names and descriptions
- User reviews
- Contact information
- Social media posts
5. Structured Storage
Information is saved in usable formats:
- CSV or Excel files
- SQL databases
- JSON formats for APIs
- Business Intelligence systems
Competitive Advantage
Automated collection can be up to 20 times faster than manual processes, eliminating human errors and enabling real-time updates.
Compared to manual or DIY work, automated scraping can be up to 20 times faster and much more accurate.
Real-World Examples by Industry
E-commerce and Retail
Application: Competitor price monitoring and dynamic pricing adjustment.
Use case: Marketplace sellers extract competitor listing data to optimize their prices in real-time and maintain competitiveness.
Impact: Approximately 80% of e-commerce companies use some form of automated price monitoring according to industry studies.
Social Media Analysis
Application: Trend detection, sentiment analysis, and influencer identification.
Use case: Brands monitor mentions, hashtags, and comments to understand public perception and adjust marketing strategies.
Impact: Companies that track social media sentiment can respond up to 3 times faster to reputation crises.
Business Intelligence and Lead Generation
Application: B2B prospecting, contact enrichment, and competitive analysis.
Use case: Sales teams collect information from business directories, LinkedIn, and corporate websites to build qualified prospect lists.
Travel and Tourism
Application: Price aggregation and service comparison.
Use case: Comparison sites gather rates for hotels, flights, and travel packages from multiple platforms to offer users the best options.
Known example: Metasearch engines that simultaneously query Booking.com, Airbnb, Expedia, and other platforms.
Artificial Intelligence and Data Science
Application: Creating datasets for training machine learning models.
Use case: Researchers collect thousands of images, texts, or structured information to train AI algorithms.
Trend: More than 60% of machine learning projects depend on data pulled from public online sources.
Market Research
Application: Customer review analysis, product features, and consumption patterns.
Use case: Companies analyze opinions on Amazon, Trustpilot, or specialized forums to improve products or detect market opportunities.
A clear case study is the Amazon Sellers often extract data from competitors’ listings to adjust their prices in real time. Or the use of price comparison sites on travel sites like Booking.com, Tripadvisor, or Airbnb to help customers find better deals, promotions, and services for accommodations or travel packages. 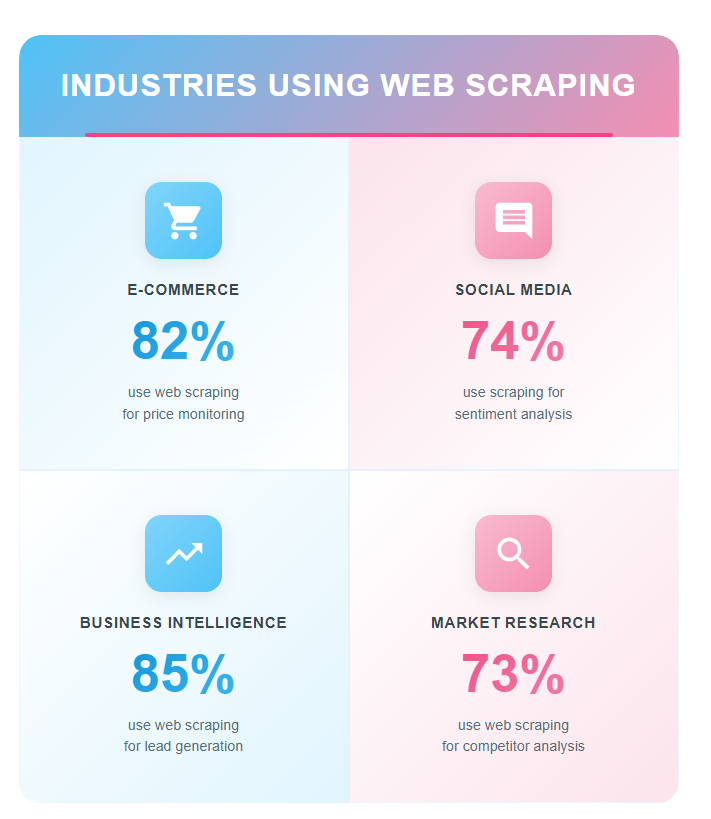
When Your Company Should Consider This Technology
Automated extraction is a strategic solution when you need:
Signs You Need This Approach
- Constant competitive monitoring – Your team spends hours manually reviewing competitor prices or products
- Real-time trend analysis – You need to detect market changes or sentiment before the competition
- Massive lead generation – Your sales team constantly requires updated prospect data
- Inventory validation – You need to verify product availability across multiple platforms
- Continuous market research – You regularly analyze reviews, forums, or media to understand your audience
- Data enrichment – Your databases need updating with external information
Demonstrable Impact
According to specialized consulting analysis, companies implementing automated collection reduce operational costs between 30% and 50% compared to manual processes, while increasing insight generation speed up to 20 times.
According to IDC, companies that implement automated data extraction reduce their operating costs by 30% to 50% compared to manual processes.
Recommended Implementation Process
Phase 1: Identification
- Map internal processes with repetitive manual collection
- Quantify invested hours and associated costs
Phase 2: Pilot Test
- Start with a small, well-defined project
- Measure results: time saved, accuracy, insights obtained
Phase 3: Scalability Evaluation
- If data volume is high, consider professional services
- Evaluate in-house vs. outsourcing solutions based on technical capabilities
Phase 4: Integration
- Connect extracted information with BI tools (Tableau, Power BI)
- Automate reports and dashboards for real-time decisions
Phase 5: Compliance
- Establish internal ethical use policies
- Document sources and extraction methods
- Periodically review legal compliance
Is Automated Data Collection Legal? Legal and Ethical Aspects
Yes, when done responsibly. Extracting public data is generally legal, but must be performed with respect to regulations and policies.
Legal Framework and Best Practices
Permitted Practices
- Collecting public information without registration
- Respecting the site’s
robots.txtfile - Implementing rate limiting (not overloading servers)
- Using data for internal analysis or research
Important Considerations
1. Robots.txt Compliance This file indicates which areas of a website allow automated collection. Respecting these directives is considered good practice.
2. Privacy Regulations
- GDPR (Europe): Don’t extract personal data without consent
- CCPA (California): Similar to GDPR for California residents
- Local legislation: Check country-specific regulations
3. Terms of Service Some sites explicitly prohibit automated extraction in their terms. Violating these agreements can have legal consequences.
4. Technical Considerations
- Don’t saturate servers with massive requests
- Identify your bot appropriately (User-Agent)
- Avoid circumventing security measures like CAPTCHAs
Relevant Legal Cases
Legal precedents in the United States (hiQ Labs vs. LinkedIn) have established that collecting public data is generally legal, but the landscape continues to evolve.
Professional recommendation: Consult with a legal expert before implementing large-scale operations, especially if data involves personal information or sites with restrictive terms.
FAQs
What does scraping mean in data analysis?
It is the process of converting unstructured website content into structured data for in-depth analysis.
What is the difference between a web scraper and web scraping?
A web scraper is the tool. Web scraping is the process.
Is scraping legal for businesses?
Yes, as long as data protection regulations and website policies are followed.
Which industries are most commonly used?
E-commerce, tourism, finance, marketing, and technology startups.
Conclusion: Your Web Scraping Decision-Making Strategy
As a critical conclusion, aligned with these actions, this technology in 2025 has ceased to be a technical curiosity and has become a strategic advantage. Organizations that master data extraction at scale will lead in competitive intelligence, customer experience, and digital transformation. “In our experience leading web scraping services projects across multiple industries, we have found that the combination of specialized scraping software and customized website data extraction strategies makes a difference in a business’s competitiveness“.
Ready to boost the competitive advantages of automated data extraction in your company?
Need reliable data without the technical hassle?
Scraping Pros handles everything—from scraper development to delivery. No code, no infrastructure, no maintenance.

