List Crawling vs Web Scraping: Strategic Data Collection Methods Analysis
In today’s markets, where information circulates at algorithmic speed, competitive advantage no longer depends on having more data, but on knowing how, when, and why to collect it. Leading companies don’t improvise their data extraction strategy: they design data infrastructures aligned with their business objectives, growth rate, and risk tolerance.
In this context, the traditional debate between web crawling and web scraping is insufficient. It’s not about choosing one technique “better” than the other, but about understanding the role each plays within a results-oriented market intelligence architecture. At Scraping Pros, we work daily with global organizations competing in highly dynamic markets, and the difference between leadership and lagging behind is almost always explained by a structural decision: how they collect their data.
Data Advantage as a Strategic Asset
Data is an asset only when it generates actionable decisions before the competition. Collecting information without a clear strategic framework produces volume, but not advantage. True data advantage emerges when an organization can map its competitive landscape, detect early warning signs, and delve deeper where the business value justifies it.
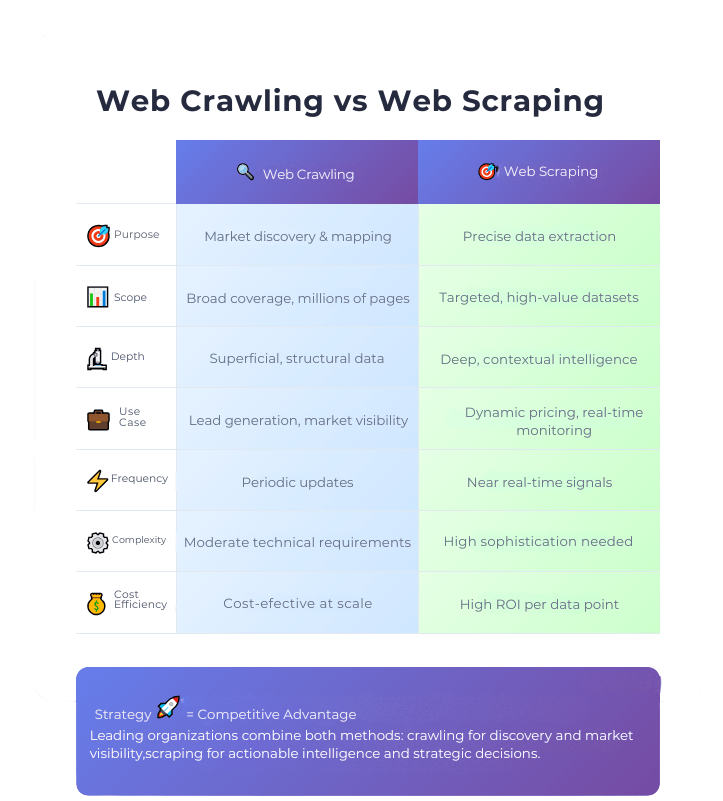
From this perspective, crawling and scraping are not isolated technologies, but rather complementary tools within the same system. Crawling allows you to understand the terrain; scraping allows you to exploit opportunities. Companies that dominate their market intentionally combine both capabilities, adjusting coverage, depth, and frequency according to the data lifecycle. Scraping Pros supports its clients precisely at this critical point: translating business objectives into robust and scalable data collection architectures, avoiding both under-extraction (lack of visibility) and over-extraction (unnecessary costs and noise).
List Crawling: When Coverage Creates Strategic Visibility
List crawling is the ideal technique when the goal is to understand a market in its entirety, not to analyze it in detail. Through the systematic exploration of categories, directories, indexes, and navigation structures, crawling allows you to build a panoramic view of the competitive ecosystem.
This approach is especially valuable in the discovery phase, when a company needs to identify relevant players, map segments, detect new market entries, or generate broad databases for lead generation. In these scenarios, coverage is more important than depth, and crawling offers a cost-benefit ratio that’s hard to match.
However, massive crawling also has clear limitations. The data is often superficial, heterogeneous, and requires further processing to acquire real value. Therefore, mature organizations don’t stop at crawling but use it as an initial layer of intelligence.
At Scraping Pros, we design distributed and incremental crawling systems capable of updating large volumes of information without overloading infrastructure or violating access policies, laying the groundwork for much more precise subsequent analysis. This approach has already proven its value across multiple industries and geographies.
A) In Latin America, a regional retail and consumer goods company used continuous crawling of marketplaces and competitor chain websites to map more than 120,000 active SKUs. The system enabled the detection of assortment expansions and category changes weeks before key sales campaigns, allowing for early adjustments to pricing and supply before these signals were visible in traditional market reports.
B) In the United States, a private equity fund focused on B2B services implemented structural crawling of industry directories, corporate websites, and bidding portals to identify rapidly growing companies within specific industry niches. From this layer of visibility, the team was able to prioritize acquisition targets and then delve deeper with selective scraping of critical operational metrics, significantly reducing the initial due diligence time.
C) Also in Latin America, a commercial real estate platform used incremental crawling of real estate portals and public registries to monitor supply dynamics, turnover, and the emergence of new developments in multiple cities. This coverage allowed them to identify micro-markets with structural changes in inventory, which were then analyzed in depth by scraping prices, contractual terms, and tenure.
Web Scraping: Precision, Context, and Actionable Intelligence
When the strategy demands depth, context, and high-impact signals, web scraping becomes indispensable. Unlike crawling, scraping allows access to layers of information not available in general listings: dynamic pricing, product variations, availability, ratings, reviews, and multiple behavioral indicators. Scraping doesn’t seek indiscriminate volume; it seeks value per request. Each data extraction has a clear purpose and is integrated into analytical pipelines designed to inform specific business decisions, from dynamic pricing to near real-time competitive monitoring.
This level of precision requires greater technical sophistication, especially when faced with anti-bot systems and dynamic web environments. Therefore, effective scraping depends not only on tools, but also on architecture, operational expertise, and a deep understanding of the target audience.
“Scraping Pros operates global scraping services with a focus on stability, continuity, and return on investment, enabling its clients to access critical data even in highly secure environments”.
Crawling vs. Scraping: The Wrong Question
Framing the discussion as crawling versus scraping is a conceptual error. The correct question is how to design a data collection architecture that evolves with the business. Leading companies don’t commit to a single technique: they build hybrid systems that combine discovery, enrichment, and continuous updating.
In these models, crawling acts as an explorer: detecting changes, new opportunities, and market expansions. Scraping, on the other hand, acts like a scalpel: delving deeper where the economic impact justifies it. This combination allows for reduced costs, increased accuracy, and faster time between data and decision.
Scraping Pros positions itself as the architect of these infrastructures, helping organizations move from tactical solutions to strategic business intelligence systems.
Decision Framework: When to Use Crawling vs. Scraping
To correctly define when to use crawling, scraping, or both, organizations must evaluate specific strategic criteria:
- Data objective: market exploration vs. in-depth analysis
- Scale required: millions of pages vs. specific, high-value datasets
- Update frequency: periodic monitoring vs. near real-time signals
- Environmental sensitivity: open sites vs. highly secure platforms
- Time-to-value: exploratory insight vs. direct impact on pricing, sales, or strategy
The most advanced companies naturally evolve from crawling to scraping, and then to hybrid architectures, where both approaches coexist in an orchestrated manner.
From Data Collection to Market Leadership
Collecting data does not guarantee leadership. Turning data into a competitive advantage requires strategic discipline, technical architecture, and consistent execution. Organizations that master this dynamic are able to anticipate market movements, respond before their competitors, and adjust their strategy based on reliable and up-to-date information. This is where the difference between providers becomes evident. It’s not about who extracts the most pages, but about who best understands what data matters, when it changes, and how it impacts the business.
Scraping Pros works with global companies that use crawling and scraping not as ends in themselves, but as engines of business intelligence, integrated into high-level decision-making processes.
Scraping Pros: Leadership Through Data Intelligence
Scraping Pros’ leadership in this field rests on three fundamental pillars:
Strategic vision: We align collection techniques with real business objectives.
Operational excellence: We operate crawling and scraping on a global scale, with a focus on stability and continuity.
Applied intelligence: We transform data into actionable signals for pricing, research, sales, and strategy.
Conclusion: Data Advantage Is Designed, Not Collected
Market leadership isn’t accidental. It’s designed. Companies that dominate their industry understand that crawling and scraping are tools within a larger competitive intelligence strategy. The difference lies not in the isolated technology, but in the architecture, the criteria, and the speed of adaptation.
Scraping Pros has established itself as a global leader in data-driven business intelligence, supporting organizations that need more than just extraction: they need strategic clarity, operational resilience, and a sustainable advantage in increasingly competitive markets.
In a world where everyone has access to information, those who can turn it into action before the rest lead the way. That’s where Scraping Pros makes the difference.
FAQ
1. What is the difference between web crawling and web scraping?
Web crawling focuses on discovering, indexing, and mapping large volumes of URLs and site structures, while web scraping extracts specific, structured data from selected pages. Crawling builds visibility; scraping generates actionable data.
2. When should a company use list crawling instead of web scraping?
List crawling is ideal when the objective is market coverage, lead discovery, or structural mapping across many sources. It allows organizations to identify where valuable data lives before applying targeted scraping.
3. Can web crawling be used for competitive intelligence?
Yes. Competitive data crawling enables companies to monitor market presence, category expansion, directory listings, and ecosystem changes at scale, often revealing signals earlier than traditional market research.
4. Is web crawling legal and compliant for enterprise use?
When implemented correctly—respecting robots.txt, access policies, rate limits, and data protection regulations—web crawling is a compliant and widely used method for enterprise data intelligence.
5. How does distributed crawling reduce infrastructure and detection risk?
Distributed crawling spreads requests across time, geography, and infrastructure nodes, reducing load, minimizing detection, and allowing incremental updates without triggering defensive mechanisms on target sites.
6. How does Scraping Pros combine crawling and scraping in practice?
Scraping Pros uses crawling to build structured market visibility and then applies selective scraping only where high-value signals exist, optimizing cost, compliance, and data quality for enterprise intelligence use cases.

