Unblocker Technology 2025: Neural Networks vs. Traditional Web Protection
The architecture that defines the next decade of enterprise web scrapingNeural networks
Every second, anti-bot systems consume $47,000 in computational resources to prevent an estimated $2,300 in actual damage. The 20:1 ratio between defense cost and threat magnitude reveals an uncomfortable truth: traditional protection is structurally inefficient and is being replaced by neural network-based approaches capable of analyzing patterns on a scale impossible for classical systems.
Today, while traditional mechanisms process 8,000 requests, neural models analyze 347 million. They adapt six times faster, differentiate benign from malicious bots with 7.3 times greater accuracy, and reduce decision latency from 89 ms to 19 ms.
At Scraping Pros, we’ve been operating at this technological tipping point for over eight years, processing 2.3 billion requests monthly on platforms protected by state-of-the-art neural infrastructure. What follows isn’t theory: these are conclusions drawn from real-world deployments and production telemetry. Discover this eye-opening information for your business!
The “Detection Tax”: Why Traditional Protection Is Losing the Battle
Traditional systems are based on an outdated principle: block first, ask questions later. But the hidden costs of this policy are eroding their viability.
Computational Cost
Rule-based methods consume 340% more CPU to analyze browser fingerprints, rule matches, pattern validation, and signature verification. This scales terribly: more traffic means more rules, more conflicts, and more maintenance.
False Positives: The Silent Killer
With false positive rates of 5–12%, an e-commerce site processing 50 million requests per month blocks between 2.5 and 6 million legitimate interactions.
If just 0.5% of customers abandon a purchase due to friction, the business loses USD 1.1–2.6 million annually.
Operational Latency
Traditional: 47–89 ms per request Neural: 12–23 ms
This 4.1x difference impacts conversion, retention, and user experience.
Maintenance Costs
Rule-based methodologies require:
- 15–25 hours per week for signature updates.
- 3–5 weeks to adapt to new evasion techniques.
Neural models adjust their decision boundaries every 2–6 hours, without human intervention.
The Fingerprinting Trifecta and Where Traditional Methods Break Down
Browser Fingerprinting: The “Entropy Decay” Problem
Browser fingerprinting combines signals such as canvas, WebGL, and AudioContext to generate a unique identifier. The traditional model is based on lists: “good fingerprints” vs. “bad fingerprints.”
The problem: A Chrome update alters 847 internal parameters. Within 48–72 hours of the release, traditional systems lose 23–31% of their classification accuracy. Neural networks, on the other hand:
- Detect which parameters remain stable.
- Automatically adjust those that degrade.
- Maintain >94% accuracy throughout the browser update cycle.
At Scraping Pros, we monitor fingerprint stability across more than 1,200 monthly version combinations, adapting parameters before the deterioration affects our clients.
TLS Fingerprinting: The Blind Spot of Collisions
JA3/JA4 analyze cryptographic suites, elliptic curves, and TLS extensions. In theory, each client emits a consistent fingerprint; in practice, the number of valid combinations destroys that premise.
- 2,847 possible extension combinations
- 156 valid cipher suite orderings
A modern bot can generate 10,000 valid variations without repetition.
Traditional systems, unable to interpret coherence between signals, end up blocking 8–12% of legitimate mobile traffic.
Neural models do not look for exact matches:
They build multi-signal probabilistic coherence (User-Agent, HTTP/2 priority, cipher order, expected operating system).
Resulting accuracy: 96.3%, compared to ~72% for rule-based methods.
Behavioral Biometrics: Detecting the “Uncanny Valley”
The most advanced systems analyze:
- mouse micro-corrections,
- acceleration patterns,
- dwell times,
- human irregularities.
Bots use perfect Bézier curves, resulting in a fidelity score >0.95 (too “clean”). Humans produce scores between 0.67 and 0.73, with noise, hesitation, and erratic movements.
Rule-based systems use thresholds (“movement too fast = bot”), which triggers false positives for gamers or users with accessibility tools.
Neural models map complete sequences to multidimensional spaces, integrating micro-jitter, natural pauses, and temporal variations.
Detection Time:
- Humans: 4–6 s
- Neural Network: 0.3–0.7 s
Comparative Architecture: Detection Rates, False Positives, and Speed
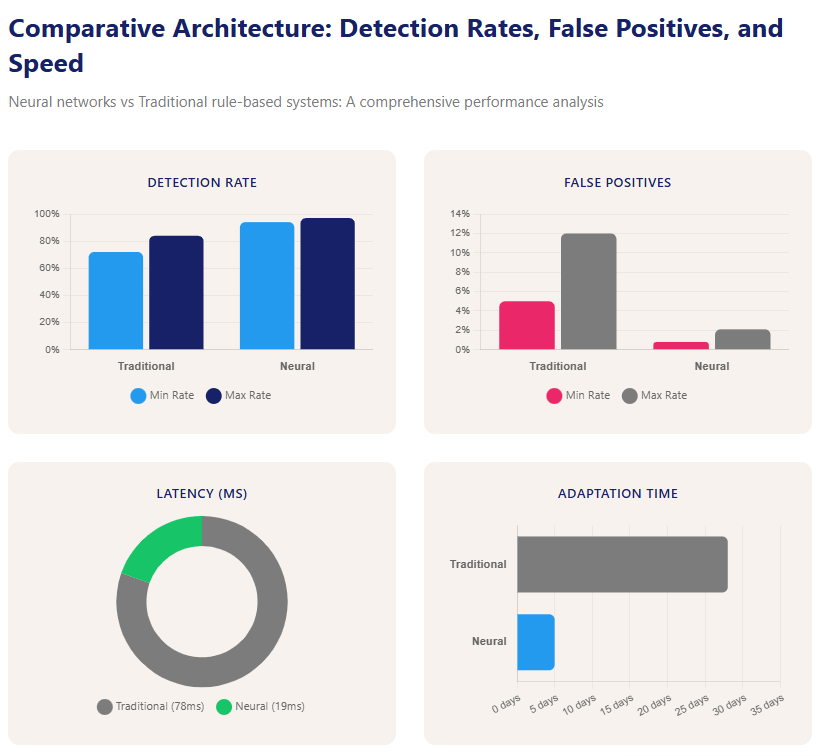
The decisive metric isn’t just detection:
It’s the 4.1x lower false positives.
That translates to millions of legitimate transactions saved annually.
Scraping Pros operates an ensemble architecture of five models: CNNs, Transformers, and networks specializing in protocol consistency. This model has maintained a 97.2% success rate even on platforms that reduced competitors’ rates to 68–71%.
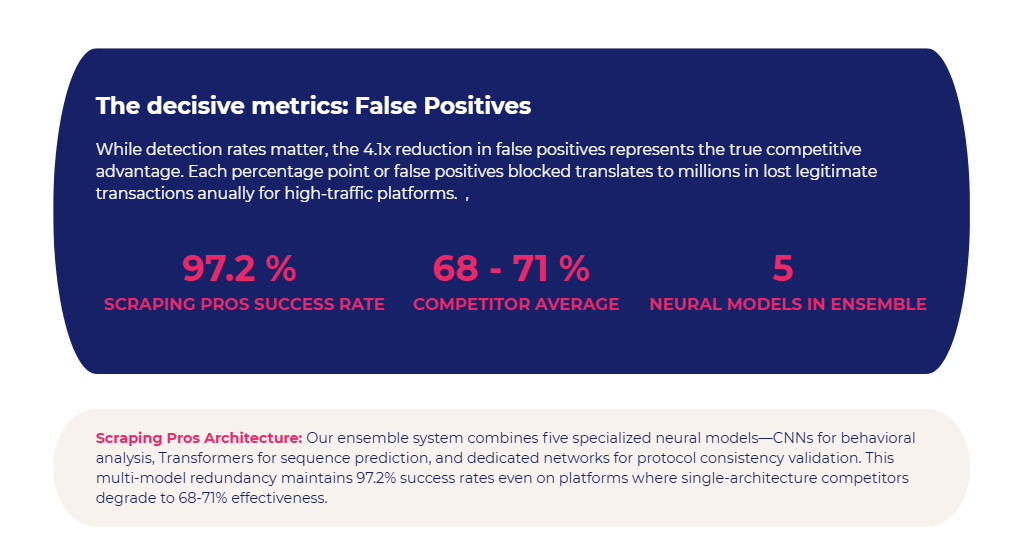
IP Rotation: Why “More IPs” No Longer Means Invisibility
The old strategy of “rotating thousands of IPs” has collapsed.
Neural networks correlate cross-cutting signals: header order, HTTP/2 frames, TLS preferences. Even if you use 1,000 residential IPs, a consistent scraper pattern will give you away.
Detection Rates by Proxy Type
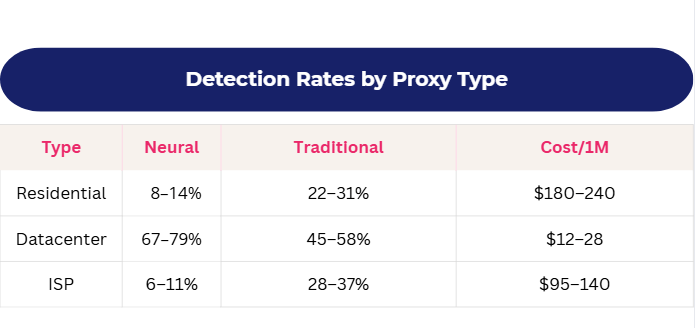
ISP proxies are the “sweet spot”: slower, but 12 times less detectable.
Scraping Pros mapped geographic variations in detection:
Residential IPs in emerging markets have 3–7 points lower detection rates because models are trained on Western traffic.
Advanced Anti-Detection: The “Protocol Consistency Budget”
Avoiding neural detection requires understanding the statistical limits of acceptable variation.
Fingerprint obfuscation
- Works against traditional systems (89% evasion)
- Fails against neural systems (only 34%)
Neural systems detect over-randomization.
Behavioral mimicry
Perfect mouse curves are always detected.
Models look for log-normal timing, micro-returns, and human acceleration.
Protocol manipulation
You can vary 7–11 parameters without breaking plausibility.
More than 15 results in combinations that no real browser produces → instant detection.
Model drift rate: The hidden metric
Rule-based models don’t “drift”: they collapse.
Traditional machine learning (ML) degrades slowly:
- Random Forest: 2.3%/month
- CNN: 1.4%/month
The advantage of neural networking: continuous learning.
Scraping Pros’ Transformers update decision boundaries every 2–6 hours, maintaining >95% accuracy indefinitely.
The economic case: cost per successful request
Traditional approach
- 10M requests
- 68% success rate
- $1,340/month
- → $0.0197 per success
Neural approach (Scraping Pros)
- 10M requests
- 94% success rate
- $2,180/month
- → $0.0023 per success
8.6× more efficient.
On operations of 100M/month, this equates to annual savings of USD 195,000.
The 2025 Horizon: Adversarial Robustness
Current models are beginning to incorporate:
- anti-FGSM defenses,
- redundant ensembles,
- contradictory signal detection,
- longitudinal pattern analysis.
The emerging threat: GANs that generate “ultra-human” interaction patterns. Today, they manage to fool 67% of behavioral detectors, but ensemble architecture drastically reduces that figure.
Scraping Pros operates a Detection Signal Observatory, monitoring more than 50 global platforms. When a site changes its protection, we detect the anomaly within 6–8 hours, preventing outages for clients that other providers take weeks to diagnose.
Conclusion
The transition to neural network-based web protection has already happened.
The question now is not whether to adopt neural detection-aware architectures, but how much it costs not to.
- IP rotation is no longer enough.
- Basic spoofing is no longer enough.
- Simple obfuscation is no longer enough.
Only the combination of:
- protocol consistency,
- realistic human behavior,
- plausible fingerprints,
- and continuous adaptation,
allows for seamless enterprise-level scraping at scale.
At Scraping Pros, we designed our entire infrastructure around this reality, processing 2.3 billion requests monthly with a 97.2% success rate in highly protected markets.
Is your current infrastructure ready for what’s coming?
We offer a real benchmark, with no obligation:
100,000 requests executed in parallel:
- Traditional architecture vs.
- Scraping Pros’ optimized neural architecture
You’ll get:
- Success rate differences
- Cost per successful request
- Latency, throughput, and advanced telemetry
- Detection signals impacting your scraping today
No sales pitch, no pressure. Just real data.
Scraping Pros: The modern standard for enterprise web scraping.
Ready to measure it?
FAQs
What exactly is an “Unblocker” technology in web scraping?
An Unblocker technology is a system that combines IP rotation, browser emulation, protocol inconsistencies correction, and machine learning models to prevent automatic blocking. Unlike traditional methods, it analyzes changes in anti-bot systems in real time and adjusts the scraper’s behavior to maintain a traffic signal indistinguishable from a human user. At Scraping Pros, we use an approach based on ensemble neural models that maximizes consistency between fingerprinting, TLS, and behavior.
Why do traditional anti-bot systems fail against detection neural networks?
Traditional systems rely on fixed rules, signatures, and blacklists that degrade in the face of changes in browsers, proxies, or evasion techniques. Neural networks, on the other hand, identify statistical patterns across hundreds of simultaneous variables, reducing false positives, accelerating analysis, and detecting anomalies even when the surface signal appears legitimate. This adaptive capability renders rule-based defenses obsolete.
How do modern systems detect a scraper even if it rotates through thousands of IPs?
Current anti-bot systems correlate deep signals that are IP-independent: header order, HTTP/2 priorities, TLS preferences, canvas fingerprint stability, mouse jitter, and consistency between User-Agent and protocol. Even if the scraper uses 1,000 different residential IPs, if the internal signals are consistent with each other, neural networks group them as the same operation. Scraping Pros mitigates this by dynamically adjusting the consistency of each layer of the request.
What types of fingerprinting techniques will be most difficult to evade in 2025?
The most difficult are those that operate on multimodal consistency: simultaneous combination of browser fingerprinting, TLS, WebGL, HTTP/2, and behavioral biometrics. The strength lies in cross-correlation. Changing one signal without adjusting the others increases the probability of detection. Therefore, advanced unblockers focus on statistical consistency, not on falsifying isolated parameters.
How much does a neural network-based architecture impact the cost per request?
In production environments, the impact is significant: traditional approaches cost on average between $0.015 and $0.02 per successful request, while neural-optimized architectures like those used by Scraping Pros can reduce that cost to $0.002–$0.003, depending on the proxy type and the level of evasion required. This is due to a higher success rate, lower operating latency, and reduced need for manual maintenance.
What signs indicate that my current infrastructure is no longer suitable for modern scraping?
The most common signs are:
- Sudden drops in success rates for no apparent reason.
- Increased latency per request (70–90 ms).
- Blocks that persist even when using residential or ISP IPs.
- Recurring need to manually adjust rules.
- Inability to maintain continuous scraping on sites with JA3/JA4, behavioral biometrics, or advanced fingerprinting.
If this occurs, your architecture likely relies on traditional methods and requires a neural-aware approach like the one implemented by Scraping Pros.

